Learn the new frontend build tool Vite
Next Generation Frontend Tooling
When I need multiple different pages and create a React app that needs a backend, my go-to framework is
Next.js. But sometimes I just want to create a React app, maybe for a demo or to start a project. I used to usecreate-react-appbut these days I useVite.
Use create-vite to start a Vite project by running npm create vite@latest. You can also try Vite online on StackBlitz at https://vite.new.
Vite consists of two major parts:
- A dev server that serves your source files over native ES modules, with rich built-in features and fast Hot Module Replacement (HMR). It only needs to transform and serve source code on demand, as the browser requests it. When you debug with Vite, just looking at the network tab and every module is a request here because it doesn’t concatenate everything.
- A build command that bundles your code with Rollup, pre-configured to output highly optimized static assets for production.
Once you’ve built the app, you may test it locally by running npm run preview command. It will boot up a local static web server that serves the files from dist. It’s an easy way to check if the production build looks OK in your local environment.
Webpack and Vite
When you start the app in development, Webpack will bundle all of your code, and start the webpack-dev-server, the Express.js web server which will serve the bundled code. Within the bundled js file contains all modules for the app and need to regenerate the entire file when we change a file for HMR. It can often take an long wait to spin up a dev server, and even with HMR, file edits can take a couple seconds to be reflected in the browser.
Vite doesn’t set out to be a new bundler. Rather, it’s a pre-configured build environment using the Rollup bundler and a tool for local development. Vite pre-bundles dependencies in development mode using esbuild.
esbuild, which is written in Go, 10-100x faster than JavaScript-based bundlers, does the transpile things transforming into plain javascript. It will process and prebundle the dependencies into something works in the browser as native es-module.vite --forcewill ignore the dependency cache and reforce to process all the dependencies.
# esbuild can resolve all the imports and bundle everything into one file
esbuild script.js --bundle --minify --outfile=bundle.jsVite only support ES Modules, and parsing the native ES Modules means it will read the export and import lines from your code. It will convert those lines into HTTP requests back to the server, where it will again read the export and import lines and make new requests. Vite also leverages HTTP headers to speed up full page reloads: source code module requests are made conditional via 304 Not Modified, and dependency module requests are strongly cached via Cache-Control header.
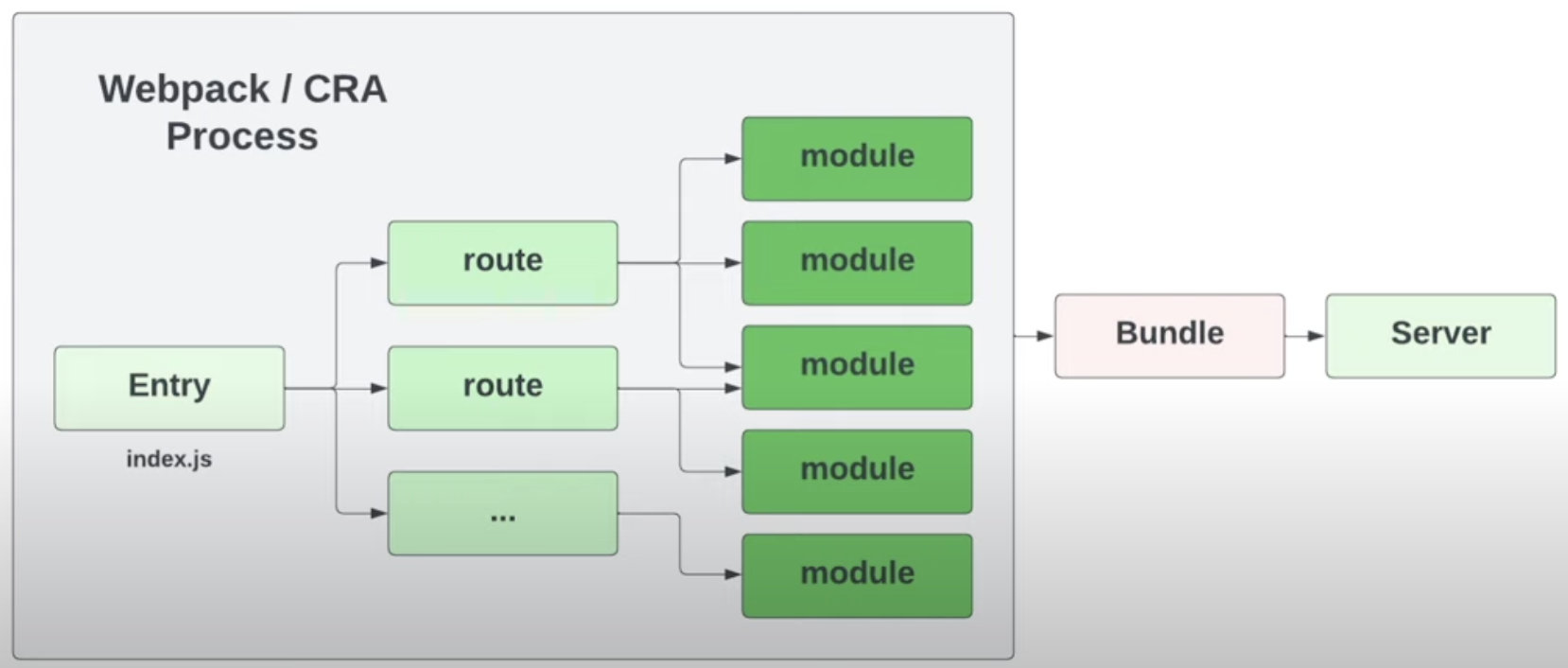
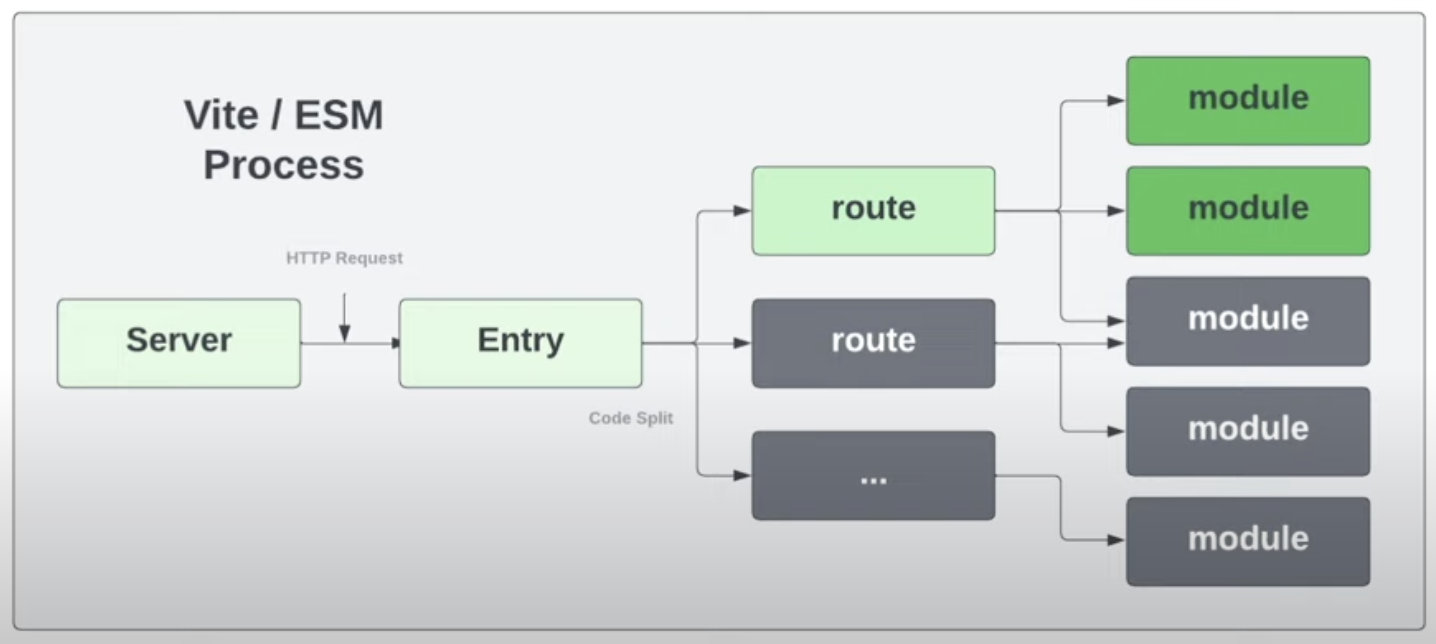
Webpack
- supported modules: ES Modules, CommonJS and AMD Modules
- dev-server: bundled modules served via webpack-dev-server using Express.js web server
- production build: webpack
Vite
- supported modules: ES Modules
- dev-server: native ES Modules served via Vite using Koa web server
- production build: Rollup
Popular Webpack plugins and their Vite equivalents
- HtmlWebpackPlugin -> vite-plugin-html
- MiniCssExtractPlugin -> vite-plugin-purgecss
- CopyWebpackPlugin -> vite-plugin-static-copy
- DefinePlugin -> define()
Issues with Vite
https://github.com/vitejs/vite/discussions/13697#discussioncomment-10241433
The page load speed for large web apps is the bottleneck in Vite’s development experience. This bottleneck isn’t related to HMR or slow Vite compilation speeds—both of these are already fast enough. The underlying cause is Vite’s mechanism of sending ES modules directly to the browser.
Vite’s current unbundle mechanism is not suitable for large web app development, as it reloads a large number of code files and generates numerous requests on every page refresh. While Vite has Dependency Pre-Bundling to solve third-party dependency issues, for large web app, our own codebase is also substantial. When a page has 500 source files simultaneously, the development experience becomes terrible.
Features
NPM Dependency Resolving
- Pre-bundle them to improve page loading speed and convert CommonJS / UMD modules to ESM. The pre-bundling step is performed with esbuild.
- Rewrite the imports to valid URLs like
/node_modules/.vite/deps/my-dep.js?v=f3sf2ebdso that the browser can import them properly. - Vite caches dependency requests via HTTP headers.
- This only happens during development. In production, a real full bundle is created via Rollup.
By default, Vite will automatically analyze the project and draw a “optimization boundary” around all the package imports. The “optimization boundary” is used to pre-bundle the dependencies into ESM and put them into node_modules/.vite/deps. Option optimizeDeps.include and optimizeDeps.exclude are used to opt-in/opt-out certain package imports to/from the “optimization boundary”.
To better understand how it works, you can open the browser DevTools and check the “Network” panel. You will see all the requests to the Vite dev server. And some of them point to the node_modules/.vite/deps folder.
// originally 'react'
import react from "/node_modules/.vite/deps/react.js?v=<hash>";
// originally 'react-dom/client'
import reactDom_client from "/node_modules/.vite/deps/react-dom_client.js?v=<hash>";
// import cjs file
import { foo as fooCjs } from "foo/foo-cjs.cjs";
// The above import has been resolved into this
import foo_fooCjs from "/node_modules/.vite/deps/foo_foo-cjs__cjs.js?v=<hash>";
const fooCjs = foo_fooCjs["foo"];TypeScript
- Vite supports importing
.tsfiles out of the box. - Only performs transpilation on
.tsfiles and does NOT perform type checking. It assumes type checking is taken care of by your IDE and build process. For production builds, you can runtsc --noEmitin addition to Vite’s build command. During development, use vite-plugin-checker if you prefer having type errors directly reported in the browser. - Vite uses esbuild to transpile TypeScript into JavaScript which is about 20~30x faster than vanilla
tsc.
While Vite and other tools handle the actual transpilation of TypeScript to JavaScript, they don’t provide type checking out of the box. This means that you could introduce errors into your code and Vite would continue running the dev server without telling you. Fortunately, we can configure TypeScript’s CLI to allow for type checking without interfering with our other tools. By setting
noEmitto true, this makes TypeScript act more like a linter than a transpiler.
CSS
- Importing
.cssfiles will inject its content to the page via a<style>tag with HMR support. - Vite is pre-configured to support CSS
@importinlining viapostcss-import. - Vite does provide built-in support for
.scss,.sass,.less,.stylusfiles. There is no need to install Vite-specific plugins for them, but the corresponding pre-processor itself must be installed.
Static Assets
- Importing a static asset will return the resolved public URL when it is served. The image is included in the module graph. (What get imported it’s just the path to the file, not the actual image.) For example, importing imgUrl will be
/img.pngduring development, and become/assets/img.2d8efhg.pngin the production build.url()references in CSS are handled the same way. - Common image, media, and font filetypes are detected as assets automatically.
- If you have assets that are must retain the exact same file name (without hashing) or you simply don’t want to have to import an asset first just to get its URL, then you can place the asset in a special
publicdirectory under your project root. Assets in this directory will be served at root path/during dev, and copied to the root of the dist directory as-is.
Configuring Vite
When running vite from the command line, Vite will automatically try to resolve a config file named vite.config.js inside project root.
If the config needs to conditionally determine options based on the command (dev/serve or build), it can export a function instead. In Vite’s API the command value is serve during dev (in the cli vite, vite dev, and vite serve are aliases), and build when building for production. For a full list of CLI options, run npx vite --help in your project.
- Environmental Variables can be obtained from
process.envas usual. rootis project root directory whereindex.htmlis located, default isprocess.cwd().server.portto specify server port, default is5173.server.proxyto configure custom proxy rules for the dev server.build.outDirto specify the output directory, default isdist.
More about Vite config: https://vitejs.dev/config
Using Plugins
Vite can be extended using plugins, which are based on Rollup’s well-designed plugin interface with a few extra Vite-specific options. To use a plugin, it needs to be added to the devDependencies of the project and included in the plugins array in the vite.config.js config file.
Vite aims to provide out-of-the-box support for common web development patterns. A lot of the cases where a plugin would be needed in a Rollup project (https://github.com/rollup/plugins) are already covered in Vite. You can also check out awesome-vite plugins from the community.
Env Variables
Vite exposes env variables on the special import.meta.env object. Some built-in variables are available in all cases like import.meta.env.MODE.
Vite uses dotenv (.env) to load additional environment variables, and the loaded env variables are also exposed to your client source code via import.meta.env. To prevent accidentally leaking env variables to the client, only variables prefixed with VITE_ are exposed to your Vite-processed code.
The import.meta meta-property exposes context-specific metadata to a JavaScript module. It contains information about the module, such as the module’s URL. import.meta is available in JavaScript modules; using it outside of a module is a syntax error.
For example, import.meta.url is a native ESM feature that exposes the current module’s URL. Using new URL('.', import.meta.url) gets the directory URL.
import.meta.globto import multiple modules from the file system is a Vite-only feature and is not a web or ES standard. It is a way to import many files at once using glob patterns to find matching file paths.
// only in Vite
const rawInput = import.meta.glob([
'./basic/**/*.*',
'./basic/**/.npmrc',
], {
as: 'raw',
eager: true,
})
// 1. Add this into Vite setup
const mdxFiles = import.meta.glob("./content/**.mdx");
// 2. and it compiles to
{
"./content/foo.mdx": () => import("./content/foo.mdx"),
"./content/bar.mdx": () => import("./content/bar.mdx"),
}From Vue CLI to Vite
Vue CLI is in Maintenance Mode. For new projects, it is now recommended to use create-vue to scaffold Vite-based projects.
- Remove Vue CLI related dependencies in
package.json. - Remove
sass-loaderas Vite provides built-in support for the most common pre-processors out of the box. - Add Vite as a dependency, as well as the Vue plugin for Vite.
- With the Vite plugins installed, remove the
vue-template-compileras that’s handled by the Vite Vue plugins. - Vite is a next generation build tool, let’s proceed optimistically by only supporting the most modern browsers. Practically speaking, this means that we can remove Babel.
- Add a Vite config file
vite.config.jsin the root of the project. Import the Vue plugin and set@importalias there. - Contrary to the Vue CLI, Vite actually puts the
index.htmlfile in the root of the project instead of the public directory, so you’ll need to move it. And the JavaScript application is no longer auto injected so we need to include it like<script type="module" src="/src/main.js"></script>. - Change the old
vue-cli-servicecommands to Vite specific commands inpackage.json. - You can no longer access environment variables on a
process.envvariable. Instead they can be found onimport.meta.env. - Remove all the magic comments for naming your dynamic imports as these are webpack specific comments (e.g.
import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ "../views/About.vue")) and don’t mean anything to Vite. Vite will automatically name your chunk based off of the original.vuefile name combined with a hash.
