Understand the event loop
Inside look at a browser
A process can be described as an application’s executing program. A thread is the one that lives inside of process and executes any part of its process’s program. Chrome has a multi-process architecture and each process is heavily multi-threaded. The renderer process is responsible for everything that happens inside of a tab. In the most case, you can imagine each tab has its own renderer process, but when Chrome hits the limit, it starts to run multiple tabs from the same site in one process.
In a renderer process, the main thread is where a browser processes user events and paints. By default, the browser uses a single thread to run all the JavaScript in your page (sometimes parts of your JavaScript is handled by worker threads if you use a web worker or a service worker), as well as to perform layout, reflows, and garbage collection. This means that long-running JavaScript functions can block the thread, leading to an unresponsive page and a bad user experience. Frame drop happens when the main thread is too busy with running our JavaScript code so it doesn’t get the chance to update the UI so the website freezes.
Compositor and raster threads are also run inside of a renderer processes to render a page efficiently and smoothly. The benefit of compositing is that it is done without involving the main thread.
Everything outside of a tab is handled by the browser process. The browser process has threads like the UI thread which draws buttons and input fields of the browser, the network thread which deals with network stack to receive data from the internet, the storage thread that controls access to the files and more. For example, in the process of a navigation flow, the network thread tells UI thread that the data is ready, UI thread then finds a renderer process to carry on rendering of the web page.
To open the Chrome Task Manager, click on the three dots icon in the top right corner, then select ‘More tools’ and you can see ‘Task Manager’. With this tool, you can monitor all running processes (CPU, memory, and network usage of each open tab and extension) and stop processes that are not responding.
Site Isolation (per-frame renderer processes) is a feature in Chrome that runs a separate renderer process for each cross-site iframe.
Event loop
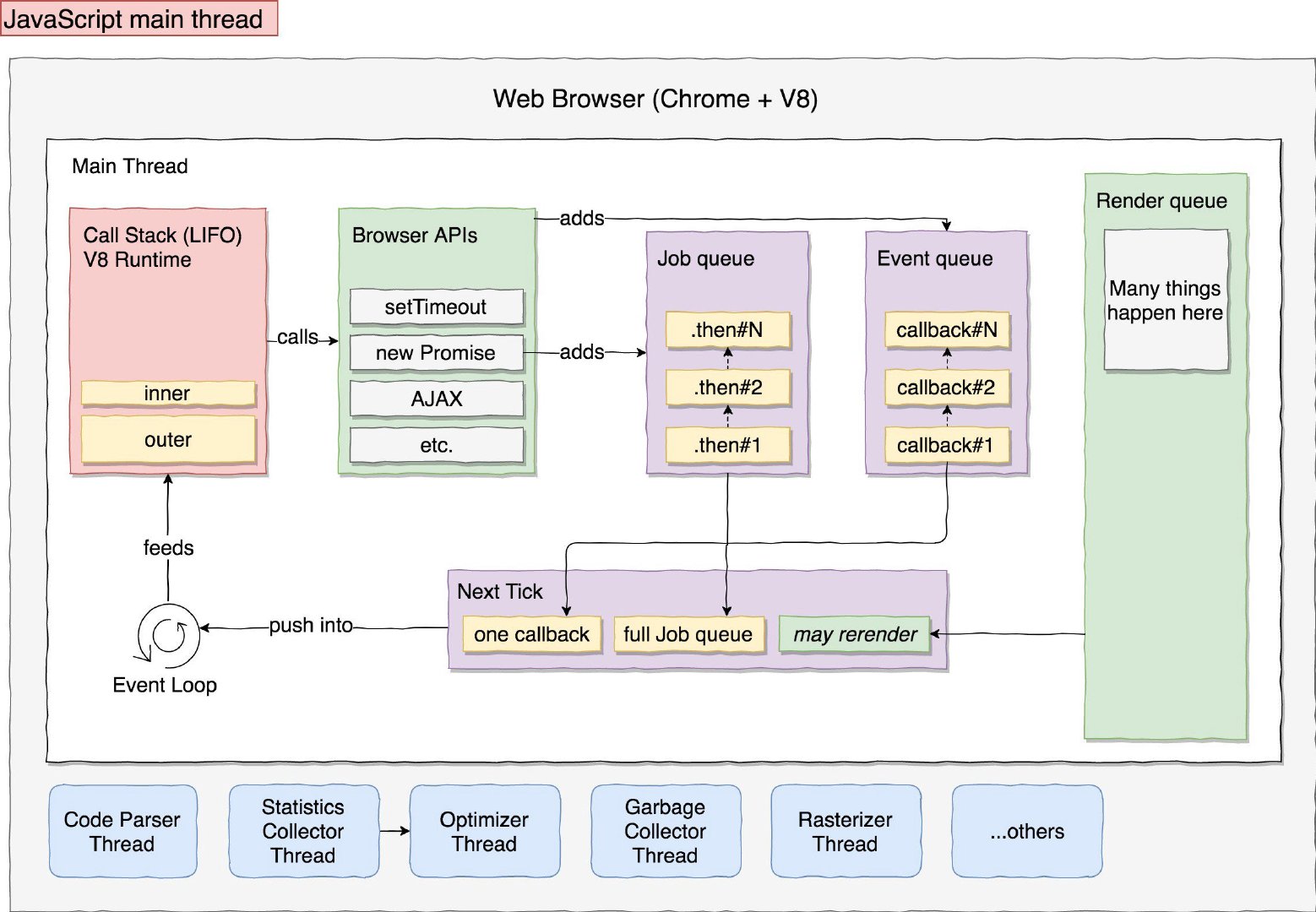
-
Stack
A single call stack in which it keeps track of what function we’re currently executing and what function is to be executed after that. When we execute an infinite loop, everything on the screen just freezes, this is because the main thread is blocked doing the infinite loop and render tasks never get a chance to come in. -
Heap
Objects are allocated in a heap which is just a name to denote a large (mostly unstructured) region of memory. -
Web APIs
A number of powerful functions and interfaces exposed to us by the browser. These web APIs enhance JS and give it the ability to do all the powerful things like Network requests, DOM manipulation, Bluetooth, Location, setTimeout… In case of callbacks they will add your callback to the Callback queue, instead, in case of a then (promise’s method), your code will be added to the Job queue. -
Task Queue
Also known as Callback Queue, which is a list of messages to be processed. Each message has an associated callback function which gets called in order to handle the message. Important to remember that when you have asetTimeoutand a delay, it’s not the delay until it gets moved onto the call stack. It’s the delay until it gets moved to the task queue. -
Micro-Task Queue
Also known as Job Queue, which is reserved for promise’s thens. It is a prioritized queue, which means “execute this code later (= asynchronously), but as soon as possible (= before the next Event Loop tick)”. After executing every task, the event loop will go to microtask queue and check if something is there and if it is then it will execute all of them. -
Render Queue
Takes care of tasks to be done before every screen update or repaints. This process is sometimes referred also as critical rendering path. Browsers generally are set to repaint around 60 times every second (60FPS), but it can happen at this speed only when the main thread is idle or the call stack is empty. -
Event Loop
The Event Loop is a constantly running process and it has one simple job — to monitor the Call Stack and the Queues. If the Call Stack is empty, it will take the first event from the queue and push it to the Call Stack. Node.js and Chrome do not use the same event loop implementation. Chrome/Chromium useslibevent, while Node.js useslibuv. Check out A Complete Visual Guide to Understanding the Node.js Event Loop.
The difference between the task queue and the microtask queue is simple but very important:
- When executing tasks from the task queue, the runtime executes each task that is in the queue at the moment a new iteration of the event loop begins. Tasks added to the queue after the iteration begins will not run until the next iteration. (setTimeout, DOM events, requestAnimationFrame)
- Each time a task exits, and the execution context stack is empty, each microtask in the microtask queue is executed, one after another. The difference is that execution of microtasks continues until the queue is empty—even if new ones are scheduled in the interim. In other words, microtasks can enqueue new microtasks and those new microtasks will execute before the next task begins to run, and before the end of the current event loop iteration. (Promises, queueMicrotask, MutationObserver)
setTimeout(() => console.log(1), 0);
async function async1() {
console.log(2);
await async2(); // just syntactic sugar on top of promise
console.log(3);
}
async function async2() {
console.log(4);
}
async1();
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log(5);
for (let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
i === 999 && resolve();
}
console.log(6);
}).then(() => {
console.log(7);
});
console.log(8);
/*
output:2 4 5 6 8 3 7 1
*/You may argue that setTimeout should be logged first because a task is run first before clearing the microtask queue. Well, you are right. But, no code runs in JS unless an event has occurred and the event is queued as a task. At the execution of any JS file, the JS engine wraps the contents in a function and associates the function with an event start, and add the event to the task queue. After emits the program start event, the JavaScript engine pulls that event off the queue, executes the registered handler, and then our program runs.
button.addEventListener("click", () => {
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log("Microtask 1"));
console.log("listener 1");
});
button.addEventListener("click", () => {
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log("Microtask 2"));
console.log("listener 2");
});
// If the user clicks the button:
// listener 1, Microtask 1, listener 2, Microtask 2
button.click();
// If click using JS:
// listener 1, listener 2, Microtask 1, Microtask 2
// User-triggered events run each listener in separate tasks.
// JS-triggered events run all listeners in the same task, just like normal synchronous code.process.nextTick() and setImmediate() in Node.js
A function passed to process.nextTick() is going to be executed on the current iteration of the event loop, after the current operation ends. This means it will always execute before setTimeout and setImmediate.
setImmediate() and setTimeout(0) both schedule callbacks for the next event loop iteration. In most cases, especially within I/O callbacks, setImmediate will execute before setTimeout(0), though the order can vary when called from the main thread.
A process.nextTick callback is added to process.nextTick queue. A Promise.then() callback is added to promises microtask queue. A setTimeout, setImmediate callback is added to macrotask queue. Event loop executes tasks in process.nextTick queue first, and then executes promises microtask queue, and then executes macrotask queue.
Optimize long tasks
Common advice for keeping JavaScript apps fast tends to boil down to the advice: “Don’t block the main thread” and “Break up your long tasks.”
Any task that takes longer than 50 milliseconds is a long task. When a user attempts to interact with a page when there are many long tasks, the user interface will feel unresponsive. To prevent the main thread from being blocked for too long, you can break up a long task into several smaller ones. One method developers have used to break up tasks into smaller ones involves setTimeout(). With this technique, you pass the function to setTimeout(). This postpones execution of the callback into a separate task, even if you specify a timeout of 0.
// blocks the rendering (freezes the webpage)
button.addEventListener("click", event => {
while (true) {}
});
// does NOT block the rendering
function loop() {
setTimeout(loop, 0);
}
loop();
// blocks the rendering
(function loop() {
Promise.resolve().then(loop);
})();function yieldToMain() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(resolve, 0);
});
}
// Loop over the tasks:
while (tasks.length > 0) {
const task = tasks.shift();
task();
// Yield to the main thread
await yieldToMain();
}The key here is setTimeout(resolve, 0). You’re effectively saying: “Let the main thread do other work (like paint or respond to events), then continue my work on the next macrotask.”
scheduler.yield() (in Chrome 129) provides a method for yielding control to the browser, which can be used to break up long tasks. When you await scheduler.yield(), your current JavaScript function pauses and lets the browser do other work before continuing your function later. This can be useful when you want to ensure that your JavaScript code doesn’t block the main thread and negatively impact the user experience.
- With
scheduler.yield, the continuation of work is placed at the front of the task queue. - With
setTimeout, the continuation of work is placed at the end of the task queue.
async function blocksInChunks() {
// Blocks for 500ms, then yields to the browser scheduler
blockMainThread(500);
await scheduler.yield(); // The browser scheduler can run other tasks at this point
// Blocks for another 500ms and returns
blockMainThread(500);
}This api and implementation is the result of a multi year collab effort between (Meta) the React team and (Google) Chrome, and underpins react’s concurrent mode. Now being implemented in browsers as a standard.
// Here is how you can "defer" a slow operation in JS
const onIdle = (fn) => {
if ("scheduler" in window) {
return scheduler.postTask(fn, {
priority: "background",
});
}
if ("requestIdleCallback" in window) {
return requestIdleCallback(fn);
}
setTimeout(fn, 0);
};
onIdle(() => slowFunction());